COBOL Comments
What is a Comment?
- A comment is a nonexecutable code used to insert descriptive notes about the code within the program.
- They do not impact the program execution and are ignored by the COBOL compiler.
- Comments are not just a formality, they are a powerful tool for programmers to define the purpose, logic, or any special considerations regarding the code, thereby making the code more understandable.
Comment Types
The comments are three types based on their usage, and those are -
- IDENTIFICATION DIVISION Comments.
- Full-line comments (any division).
- Inline comments (any division).
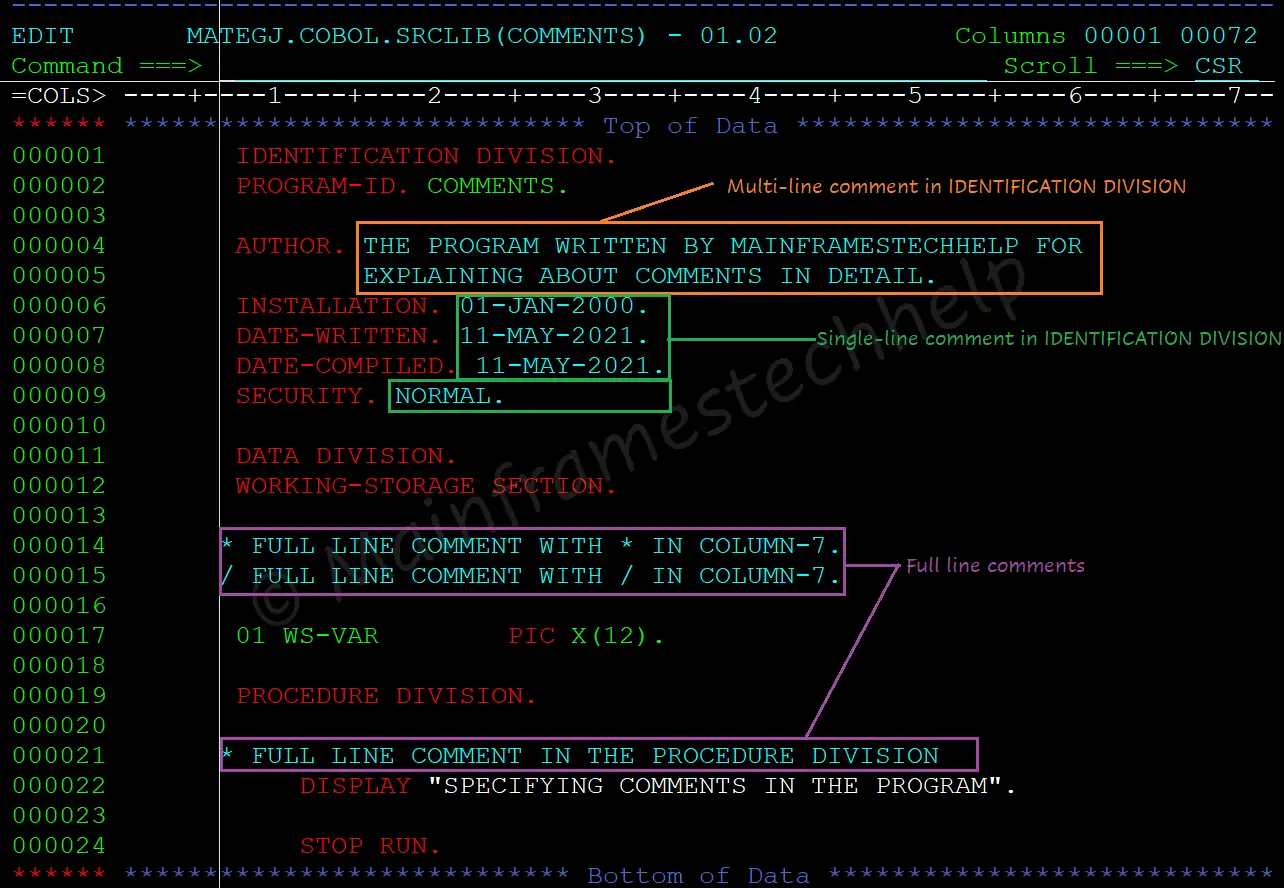
IDENTIFICATION DIVISION Comments -
IDENTIFICATION DIVISION has optional paragraphs - AUTHOR, INSTALLATION, DATE-WRITTEN, DATE-COMPILED, and SECURITY. The entries with optional paragraphs are comments.
The usage of comments in IDENTIFICATION DIVISION (All entries after keywords are comments) are -
----+----1----+----2----+----3----+----4----+----5
AUTHOR. NameOfProgrammer.
INSTALLATION. Development-center.
DATE-WRITTEN. mm/dd/yy.
DATE-COMPILED. mm/dd/yy HH:MM:SS.
SECURITY. Program-type.The comments can written in more than one line. However, it should always begin or continue in Area B. The continuation character (-) is not required while writing comments in IDENTIFICATION DIVISION.
Full line comments (Comment Line)
Any line starting with an asterisk (*) in column 7 (indicator area) is a full-line comment. Comments can be coded in any division.For example -
----+----1----+----2----+----3----+----4----+----5
* FULL LINE COMMENT WITH * IN COLUMN-7.
DATA DIVISION.Inline comments (Floating Comment)
Comments coded in the middle of any line in between 8-72 columns. An inline comment should start with a floating comment indicator (*>).
For example -
----+----1----+----2----+----3----+----4----+----5
01 WS-VAR PIC X(12). *> INLINE COMMENT Practical Example -
Scenario - Example to describe how the comments were added in COBOL programming.
Code -