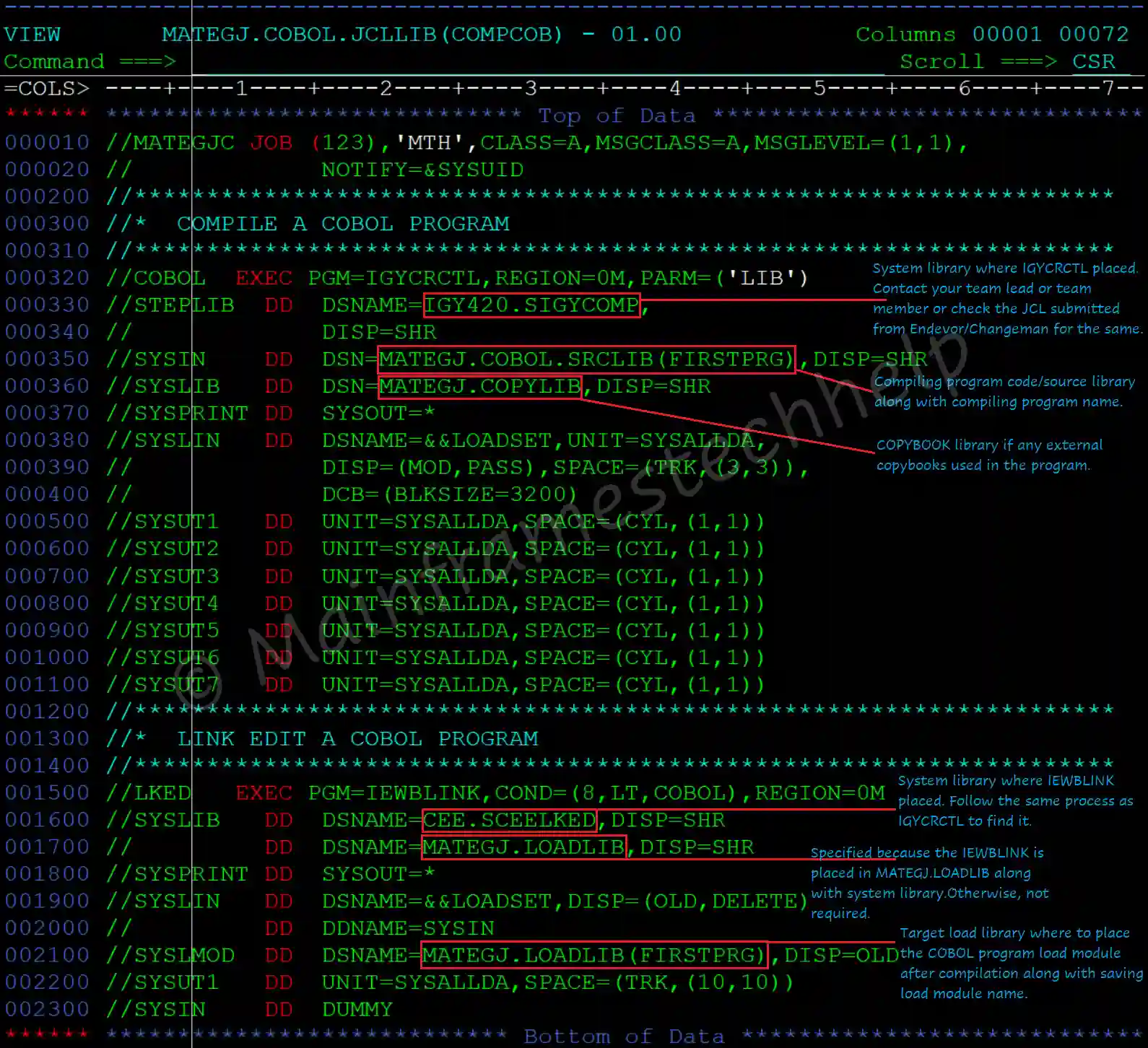
Compilation JCL for COBOL Program
There are two ways to compile the COBOL program and those are –
- Create a JCL using Version control tools - Version control tools like Endeavor or Change man are used to compile the COBOL program in a real-time environment.
- Standard alone JCL/project Specific JCL - We can also create a standard JCL to compile the program apart from version control tools. You can get a compilation JCL from your colleague/team lead in the project by specifying that you are unaware of compilation utility libraries.
The compilation JCL has two steps –
- Compiling the COBOL program. IGYCRCTL or its next version utilities are used to compile the COBOL module.
- LINK EDIT the COBOL program. IEWB or its next version utilities are used to link edit the module.
Compiling the COBOL program step -
Scenario - The following example shows the general format of JCL used to compile a program.
//jobname JOB acctno,name,MSGCLASS=1 (1)
//stepname EXEC PGM=IGYCRCTL,PARM=(options) (2)
//STEPLIB DD DSN=IGY.V6R3M0.SIGYCOMP,DISP=SHR (3)
// DD DSN=SYS1.SCEERUN,DISP=SHR
// DD DSN=SYS1.SCEERUN2,DISP=SHR
//SYSUT1 DD UNIT=SYSALLDA,SPACE=(subparms) (4)
//SYSUT2 DD UNIT=SYSALLDA,SPACE=(subparms)
//SYSUT3 DD UNIT=SYSALLDA,SPACE=(subparms)
//SYSUT4 DD UNIT=SYSALLDA,SPACE=(subparms)
//SYSUT5 DD UNIT=SYSALLDA,SPACE=(subparms)
//SYSUT6 DD UNIT=SYSALLDA,SPACE=(subparms)
//SYSUT7 DD UNIT=SYSALLDA,SPACE=(subparms)
//SYSUT8 DD UNIT=SYSALLDA,SPACE)=(subparms)
//SYSUT9 DD UNIT=SYSALLDA,SPACE=(subparms)
//SYSUT10 DD UNIT=SYSALLDA,SPACE=(subparms)
//SYSUT11 DD UNIT=SYSALLDA,SPACE=(subparms)
//SYSUT12 DD UNIT=SYSALLDA,SPACE=(subparms)
//SYSUT13 DD UNIT=SYSALLDA,SPACE=(subparms)
//SYSUT14 DD UNIT=SYSALLDA,SPACE=(subparms)
//SYSUT15 DD UNIT=SYSALLDA,SPACE=(subparms)
//SYSMDECK DD UNIT=SYSALLDA,SPACE=(subparms)
//SYSPRINT DD SYSOUT=A (5)
//SYSLIN DD DSN=&&LOADSET,DISP=(OLD,DELETE) (6)
// DISP=(MOD,PASS),SPACE=(subparms)
//SYSIN DD DSN=dsname,UNIT=device, (7)
VOLUME=(subparms),DISP=SHRExplaining JCL -
- The JOB statement specifies the job beginning.
- The EXEC statement specifies that the Enterprise COBOL compiler (IGYCRCTL) will be executed.
- The DD statement specifies the dataset where the COBOL compiler resides.
- The SYSUT DD statements specify the utility datasets that the compiler will use to process the source program. All SYSUT files should be on direct-access storage devices.
- The SYSPRINT DD statement specifies the dataset that receives output from compiler options.
- The SYSLIN DD statement specifies the output dataset that receives from the compiler step and passes it to the link-edit step.
- The SYSIN DD statement specifies the source datasset where the COBOL program code is written.
LINK EDIT the COBOL program step –
Scenario - The following example shows the general format of JCL used to compile a program.
//LKED EXEC PGM=IEWBLINK,COND=(8,LT,COBOL),REGION=0M (1)
//SYSLIB DD DSN=CEE.SCEELKED,DISP=SHR (2)
//SYSPRINT DD SYSOUT=* (3)
//SYSLIN DD DSN=&&LOADSET,DISP=(OLD,DELETE) (4)
// DD DDN=SYSIN
//SYSLMOD DD DSN=MATEGJ.LOADLIB(FIRSTPRG),DISP=OLD (5)
//SYSUT1 DD UNIT=SYSALLDA,SPACE=(TRK,(10,10)) (6)
//SYSIN DD DUMMY Explaining JCL -
- The EXEC statement specifies Link Editor (IEWBLINK) will be executed.
- The SYSLIB DD statement specifies the dataset where the IEWBLINK resides.
- The SYSPRINT DD statement defines the dataset that receives output.
- The SYSLIN DD statement specifies the dataset where the object code stored by COMPILE step.
- SYSLMOD DD statement specifies the dataset where the executable load module will be stored.
- The SYSUT DD statements specify the utility datasets that IEWBLINK will use to complete the process.
What needs to change in Compilation JCL?