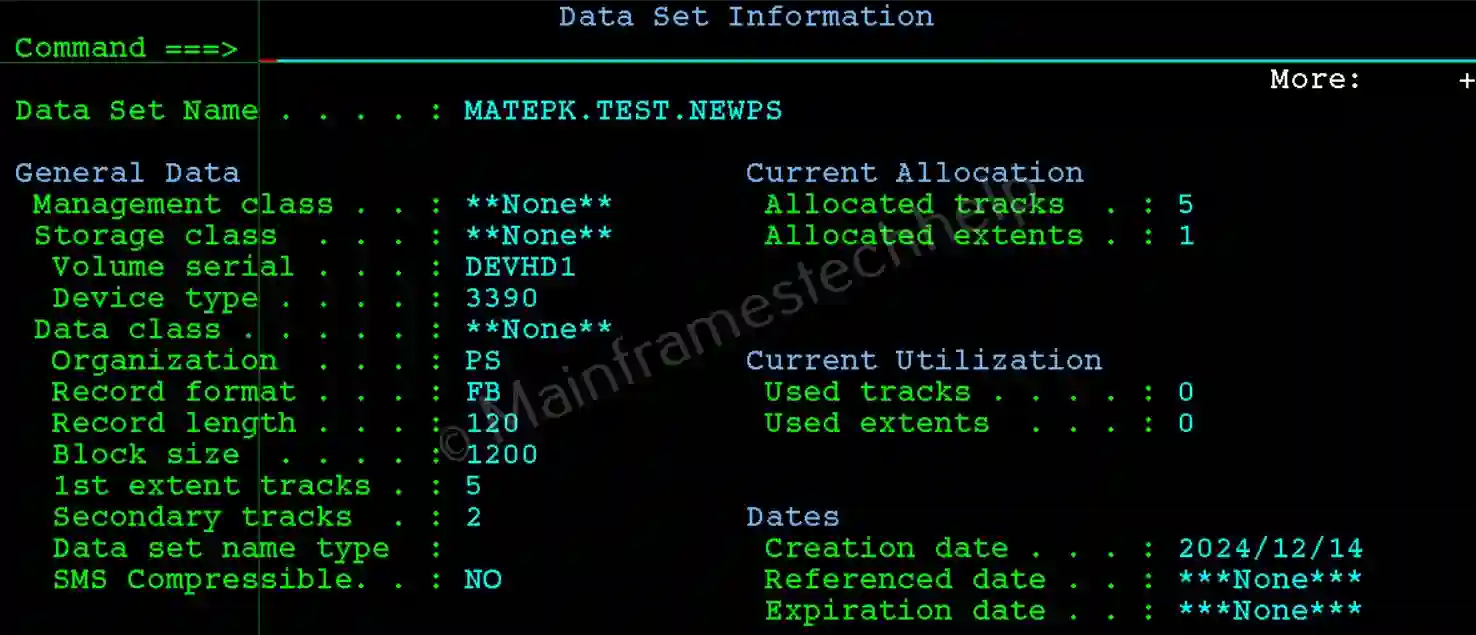
ISPF Create PS
In the IBM mainframe environment, PS (Physical Sequential) refers to a dataset where data is stored sequentially, one record after another. Creating a PS dataset is a common task performed using ISPF's Dataset Utility Panel.
Navigation - Option 3.2 (Data Set Utility) from ISPF Primary Option Menu (ISPF Home Menu).
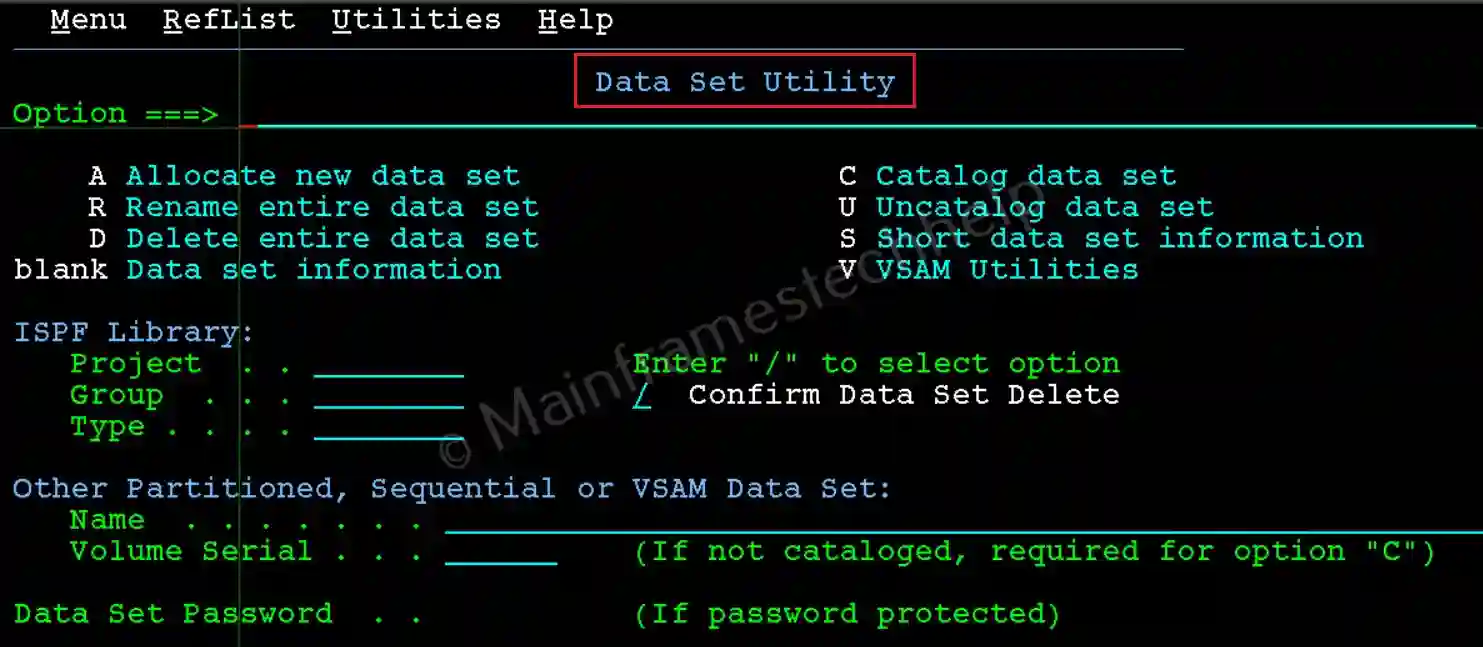
Steps to Create a PS Dataset -
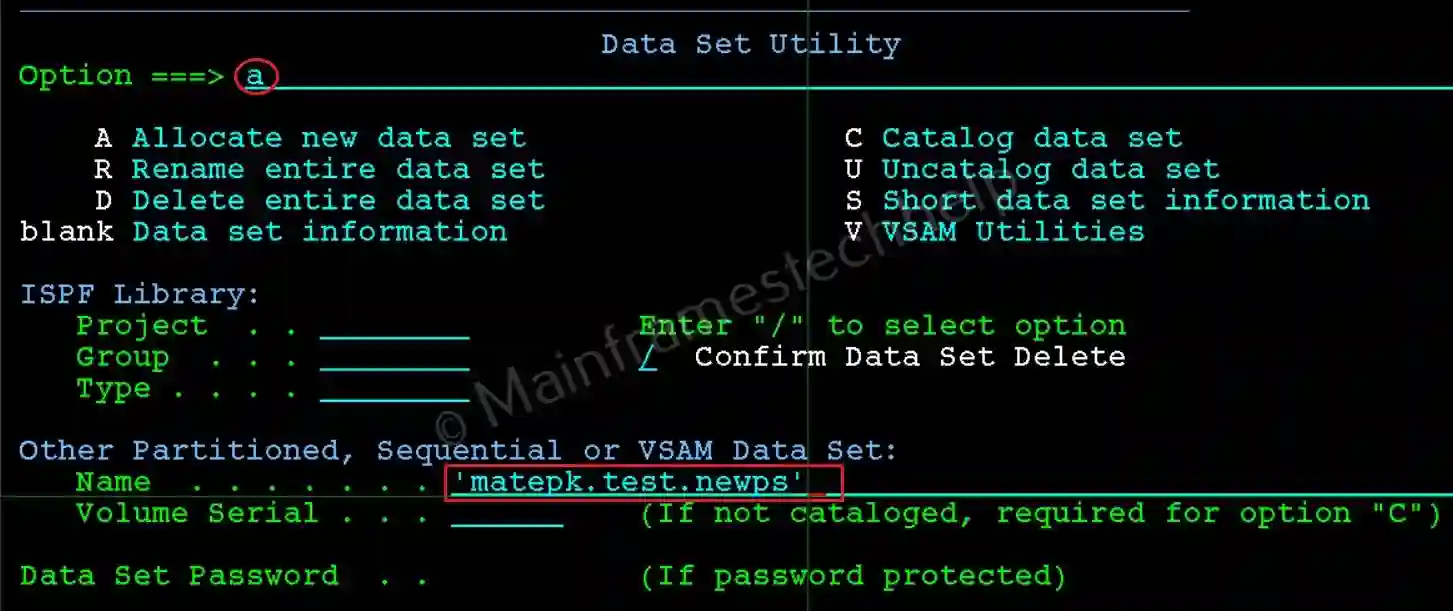
Step-1: From the Data Set Utility panel, Enter the new PS DataSet name in quotes(') in the Name field and A at the command line. Press Enter.
Step-2: Allocate New Data Set screen appear like below. Fill the required details -
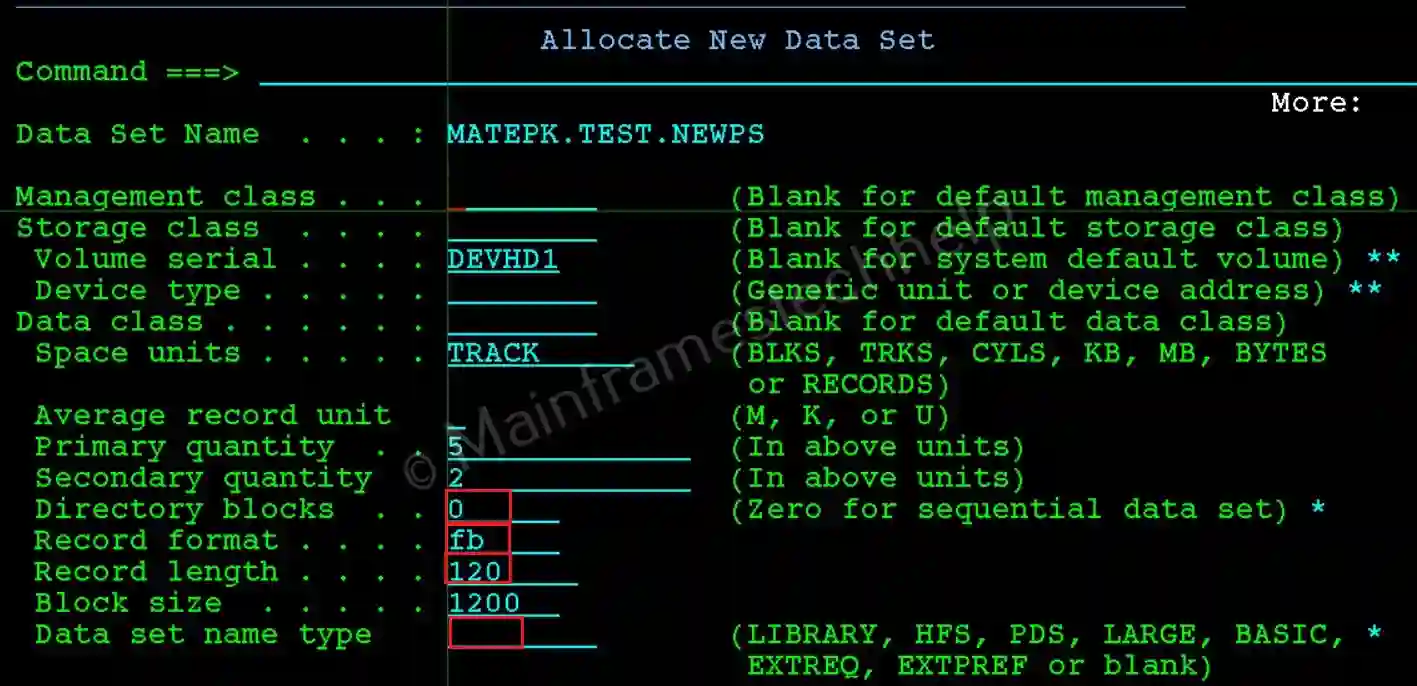
Parameters -
- Management Class: Optional. It represents a collection of management attributes defined by the storage administrator. Controls dataset retention and migration.
- Storage Class: Optional. It defines how and where a dataset is stored on the mainframe. It is managed by the Storage Management Subsystem (SMS) and determines the physical storage medium and performance requirements for a dataset.
- Volume Serial: Optional. It specifies the storage volume if required (optional for SMS-managed datasets).
- Data Class: Optional. It simplifies the allocation process by automatically specifying characteristics like space allocation, record format, block size, and record length, eliminating the need to define them manually.
- Space units: Mandatory. It specifies the type of space unit used for allocation. The available options are - BLKS, TRKS, CYLS, KB, MB, BYTES or RECORDS.
- Average record unit: Optional. It specifies the unit used to measure the average record size. The available options are - M, K or U.
- Primary quantity: Mandatory. It specifies the initial space allocated for the dataset.
- Secondary quantity: Mandatory. It specifies the additional space allocated when the primary allocation is exhausted.
- Directory blocks: Mandatory and should be 0 for PS. It determines the number of members a Partitioned Dataset (PDS) can accommodate.
- Record format: Mandatory. It specifies the format of records in a dataset (used for both PDS and PS). The available options are - F (Fixed), FB (Fixed-block), V (Variable), VB (Variable-block), and U (Unformatted) and many mor combinations.
- Record length: Mandatory. Specifies the record-length in the file.
- Block size: Mandatory. Specifies the block size. It always defines as multiples of record length.
- Data set name type: Optional. Specifies the type of the dataset. The available options are - LIBRARY, HFS, PDS, LARGE, BASIC, EXTREQ, EXTPREF or blank).
- Expiration date: Optional. It specifies the number of days a dataset can remain in the migrated stage (on TAPE) before being deleted.
- Allocate Multiple Volumes: Optional. It will be used when the file is big and can't fit on single volumne. use '/' to select the option.
Step-3: After all details are filled, hit Enter. If the allocation is successful, "Data set allocated" message shown on the right-top corner of "Data Set Utility" Screen.
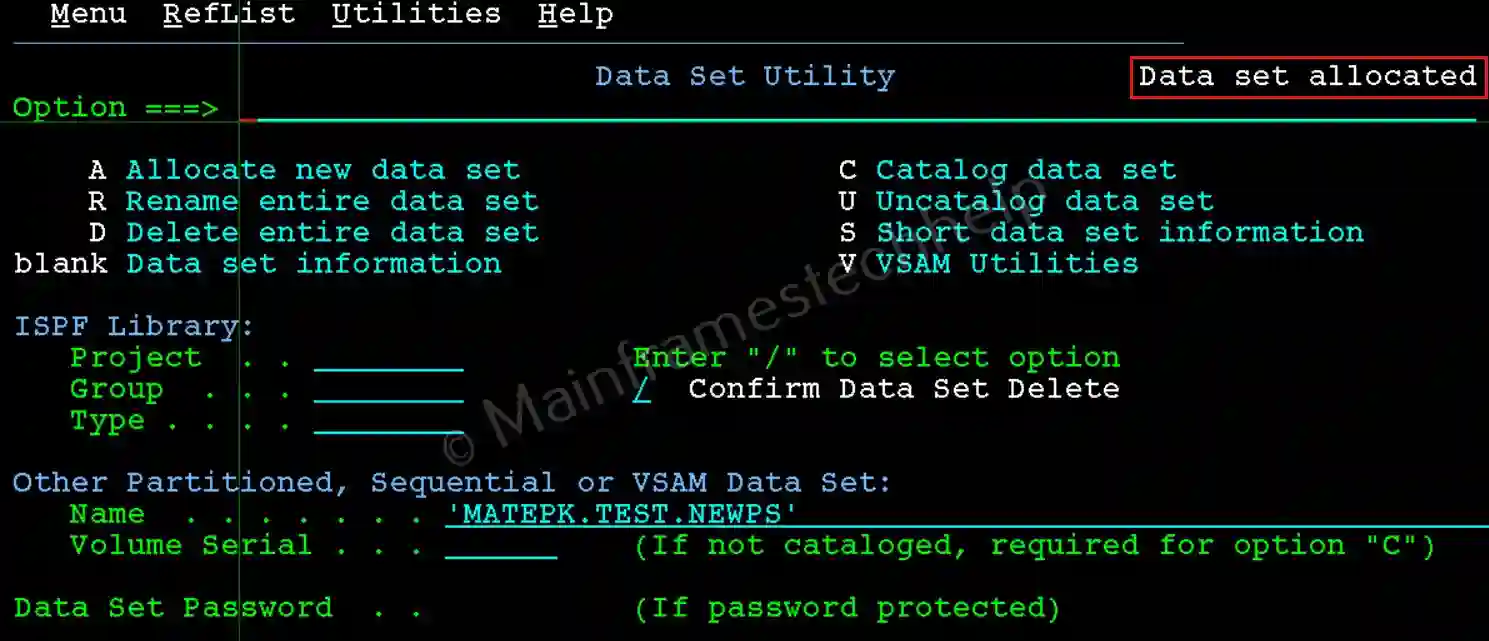
Step-4: The new PS dataset is successfully created now. To verify the PS dataset, hit Enter on the same screen (option blank). It displays the complete dataset information.