DB2 OPEN Cursor
The OPEN CURSOR statement initializes and activates a previously declared cursor. Once a cursor is declared with a SELECT statement, OPEN CURSOR executes the SELECT query, preparing the cursor to retrieve rows from the result set.
The OPEN CURSOR statement is used to activate a cursor so that it can start fetching rows. When we open a cursor:
- DB2 processes the SQL SELECT statement defined in the DECLARE CURSOR statement.
- The cursor is positioned at the beginning of the result set, ready to retrieve rows with the FETCH command.
- This allows COBOL programs to work with multiple rows from the result set one at a time without loading all rows simultaneously.
The cursor cannot fetch rows without an OPEN CURSOR because the result set has not yet been initialized.
Syntax -
EXEC SQL OPEN cursor-name END-EXEC.
- cursor_name: The name of the cursor that was previously declared with a SELECT statement. This name is used consistently throughout the cursor’s lifecycle in SQL commands such as OPEN, FETCH, and CLOSE.
Example -
Input-
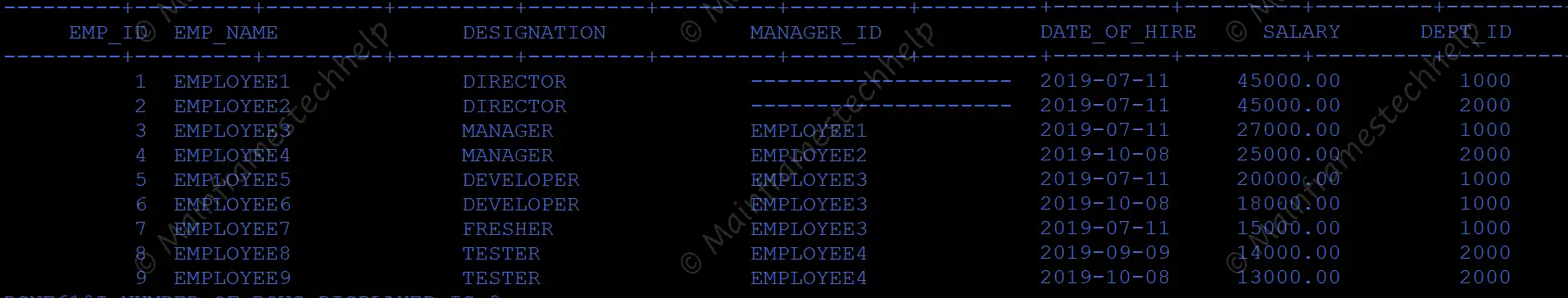
Scenario1 - Open cusor.
Code -
...
EXEC SQL
OPEN C1
END-EXEC.
...Scenario2 - Open cursor using host variables HV1, HV2 to receive two column values.
Code -
...
EXEC SQL
OPEN C2 USING :HV1, :HV2
END-EXEC.
...